Imagine the tranquil beauty of your pond, enhanced by the gentle cascade of a solar-powered fountain. It's not just about aesthetics; it's about creating a thriving ecosystem. But how do you ensure you choose therightsolar pump for your pond's unique needs? It's more than just picking the prettiest one!
Many pond owners struggle with algae blooms, stagnant water, and unhappy aquatic life. Often, the culprit is inadequate water circulation and oxygenation. Traditional pumps can be expensive to run, especially if you're off-grid. The challenge lies in finding a solar pump that provides sufficient flow, works reliably in varying weather conditions, and fits within your budget, all while being environmentally friendly.
This guide will walk you through the essential factors to consider when selecting a solar pump for your pond, ensuring optimal water circulation, oxygenation, and overall health for your aquatic ecosystem. We'll explore pond size, pump flow rate, solar panel wattage, and other key considerations to help you make an informed decision.
Choosing the right solar pump involves considering pond size, flow rate, solar panel wattage, head height, and pump type (submersible vs. surface). Proper selection promotes a healthy pond ecosystem, prevents algae blooms, and saves on energy costs. Keywords include solar pond pump, pond aeration, water circulation, pond health, and renewable energy.
Understanding Your Pond's Needs
Selecting the right solar pump starts with understanding your pond. This might seem obvious, but it's a crucial step many overlook. When I first started with my own small pond, I figured any old pump would do the trick. Boy, was I wrong! I ended up with a pump that was far too powerful, turning my tranquil pond into a miniature rapids. My poor goldfish were not impressed! That experience taught me a valuable lesson: knowing your pond is paramount.
Consider the size of your pond in gallons or liters. This will directly influence the pump's required flow rate. A general rule of thumb is to circulate the entire volume of your pond at least once every two hours. So, if you have a 1000-gallon pond, you'll need a pump with a flow rate of at least 500 gallons per hour (GPH). However, this is just a starting point. Factors like the depth of your pond, the number of fish and plants, and the amount of sunlight it receives all play a role.
Deeper ponds, for example, often require more powerful pumps to effectively circulate water from the bottom to the surface. This is essential for preventing stagnant areas and ensuring proper oxygenation throughout the pond. Similarly, ponds with a large number of fish or plants may require a higher flow rate to handle the increased biological load. Algae growth is another important factor. If your pond is prone to algae blooms, a more powerful pump can help to keep the water moving and prevent algae from taking over. It's also important to consider the aesthetic aspect. Do you want a gentle trickle or a more dramatic fountain effect? The pump's head height, which is the maximum height it can pump water, will determine the type of fountain or waterfall you can create. Think about the overall look you're aiming for and choose a pump that can deliver the desired effect.
Flow Rate and Head Height: Key Specifications
Flow rate and head height are the two most critical specifications to consider when choosing a solar pump. The flow rate, measured in gallons per hour (GPH) or liters per hour (LPH), indicates how much water the pump can move in a given time. The head height, measured in feet or meters, represents the maximum vertical distance the pump can push water. These two specifications are inversely related; as the head height increases, the flow rate decreases.
Imagine trying to drink through a very long straw. The higher you raise the straw, the harder it is to suck the liquid up. The same principle applies to pumps. As the water needs to be lifted higher, the pump has to work harder, resulting in a lower flow rate. To determine the appropriate flow rate for your pond, consider its size, depth, and the number of inhabitants. As mentioned earlier, a good starting point is to aim for a circulation rate of once every two hours. However, if your pond is heavily stocked with fish or prone to algae blooms, you may need to increase the flow rate to once per hour or even more frequently.
The head height is equally important, especially if you plan to use the pump for a fountain or waterfall. Measure the vertical distance from the pump's location to the highest point of the fountain or waterfall. This measurement will determine the minimum head height required for your pump. It's always a good idea to choose a pump with a slightly higher head height than you need, just to be on the safe side. This will ensure that the pump can deliver the desired flow rate at the required height, even under less-than-ideal conditions. Keep in mind that the head height specification provided by the manufacturer is usually the maximum height the pump can achieve, not the optimal height for flow. Look for a pump that provides a flow rate chart, which shows the relationship between flow rate and head height. This will help you to choose a pump that delivers the desired flow rate at the required head height.
A Brief History of Solar Pumps
The concept of using solar energy to power water pumps dates back to the late 19th century, driven by the need for irrigation in arid regions. One of the earliest documented solar-powered irrigation systems was developed by Auguste Mouchout in France during the 1870s. Mouchout's system used a steam engine powered by concentrated sunlight to pump water. While groundbreaking for its time, this early technology was bulky and inefficient compared to modern solar pumps.
The invention of the silicon solar cell in the 1950s marked a significant turning point in the development of solar pumps. Solar cells convert sunlight directly into electricity, making it possible to power pumps more efficiently and reliably. However, early solar cells were expensive, limiting the widespread adoption of solar pumps. As solar cell technology advanced and prices decreased, solar pumps became increasingly viable for a wider range of applications, including pond aeration and circulation.
Today, solar pumps are used extensively in agriculture, water purification, and residential applications. They offer a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional electric pumps, especially in remote areas where access to the grid is limited. The technology continues to evolve, with advancements in pump design, solar cell efficiency, and battery storage systems. These improvements are making solar pumps even more reliable, efficient, and affordable, further expanding their potential for use in various applications. While there aren't really any "myths" surrounding solar pumps, one common misconception is that they are not powerful enough for certain applications. In reality, modern solar pumps can deliver significant flow rates and head heights, making them suitable for even large ponds and water features. It's simply a matter of choosing the right pump for the job.
Unveiling the Secrets to Solar Pump Efficiency
The secret to maximizing solar pump efficiency lies in understanding the interplay between the solar panel, the pump motor, and the sunlight. A well-matched system will convert sunlight into water flow with minimal energy loss. One often overlooked aspect is the importance of proper wiring and connections. Loose connections or undersized wires can create resistance, reducing the voltage and current delivered to the pump motor. This can significantly impact the pump's performance, especially on cloudy days.
Another key factor is the orientation and angle of the solar panel. To capture the maximum amount of sunlight, the panel should be oriented towards the sun throughout the day. Adjustable mounts allow you to optimize the panel's angle based on the season and your location. In general, the panel should be angled towards the south (in the Northern Hemisphere) and tilted at an angle equal to your latitude plus 15 degrees in the winter and minus 15 degrees in the summer.
The type of pump motor also plays a crucial role in efficiency. Brushless DC motors are generally more efficient than brushed DC motors because they have fewer moving parts and less friction. They also tend to be more durable and require less maintenance. Finally, consider the pump's design. Some pumps are designed to be more efficient at specific flow rates or head heights. Choose a pump that is well-suited to your pond's specific needs. For example, if you need a high flow rate at a low head height, look for a pump that is designed for that purpose. By paying attention to these factors, you can significantly improve the efficiency of your solar pump system and ensure that it delivers optimal performance for years to come. Remember, a little extra effort in planning and installation can make a big difference in the long run.
Recommendations for Selecting Your Solar Pump
When it comes to recommending a solar pump, there's no one-size-fits-all solution. The best pump for you will depend on your specific pond size, flow rate requirements, and budget. However, I can offer some general recommendations based on my experience and research. For small ponds (up to 500 gallons), a low-wattage submersible pump with a flow rate of 100-300 GPH may be sufficient. Look for pumps with built-in filters to prevent debris from clogging the impeller.
For medium-sized ponds (500-1500 gallons), a more powerful submersible or surface pump with a flow rate of 300-800 GPH is recommended. Consider pumps with adjustable flow controls, which allow you to fine-tune the water circulation to match your pond's needs. For larger ponds (1500 gallons and up), a high-capacity surface pump with a flow rate of 800 GPH or more is typically required. Surface pumps are generally more efficient and easier to maintain than submersible pumps, especially for larger ponds. They also offer greater flexibility in terms of placement and tubing connections.
In terms of brands, I've had good experiences with pumps from reputable manufacturers like Pond Boss, Sun Sun, and ECO-WORTHY. Be sure to read reviews and compare specifications before making a purchase. It's also important to consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer. A longer warranty typically indicates a higher quality product. Finally, don't be afraid to ask for help from experts. Many online retailers and pond supply stores offer free consultations to help you choose the right solar pump for your needs. Take advantage of these resources to ensure that you're making an informed decision.
Solar Panel Wattage: Matching Power to Your Pump
Solar panel wattage is directly related to the amount of power your solar pump can generate. It’s important to understand how these two components of your solar water feature system work together. Simply put, the wattage of your solar panel needs to be sufficient to power your pump, taking into account factors like sunlight availability and the pump’s power consumption.
Choosing the right wattage isn't a guessing game. Typically, the manufacturer will specify the recommended solar panel wattage for their pump. This recommendation is based on the pump's power consumption and the typical amount of sunlight available in most regions. However, if you live in an area with frequent cloudy days or shaded conditions, you may need to increase the panel wattage to ensure that the pump receives enough power. For example, if the pump requires 20 watts and the panel is rated at 20 watts, the pump will only operate at full power when the panel is receiving direct sunlight. On a cloudy day, the panel's output may drop to 10 watts or less, causing the pump to run at a reduced speed or even stop altogether.
To compensate for this, you could choose a panel with a higher wattage rating, such as 30 or 40 watts. This will provide a buffer of power, ensuring that the pump continues to operate even under less-than-ideal conditions. It’s also essential to consider the voltage and current requirements of the pump and panel. The voltage of the panel must match or exceed the voltage of the pump. If the voltage is too low, the pump will not operate. The current of the panel must also be sufficient to meet the pump's current requirements. If the current is too low, the pump will not operate at full power.
Tips for Extending the Life of Your Solar Pump
Extending the life of your solar pump is easier than you think. With a few simple steps, you can keep your pump running smoothly and efficiently for years to come. One of the most important tips is to clean the pump regularly. Debris like leaves, algae, and sediment can clog the impeller and reduce the pump's performance. Depending on the type of pump, you may need to disassemble it to clean the impeller thoroughly. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for cleaning and maintenance.
Another important tip is to protect the solar panel from damage. The panel is the heart of the system, and if it's damaged, the pump won't work. Avoid placing the panel in areas where it could be struck by falling objects or exposed to harsh weather conditions. If possible, mount the panel on a sturdy pole or bracket to protect it from damage. Regularly check the wiring and connections to ensure that they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose connections or corroded wires can reduce the voltage and current delivered to the pump, causing it to run at a reduced speed or even stop altogether.
If you live in an area with freezing temperatures, be sure to winterize your solar pump system. Remove the pump from the pond and store it indoors in a frost-free location. This will prevent the pump from freezing and cracking. Disconnect the solar panel and store it in a safe place. If you have a battery storage system, be sure to charge the batteries fully before storing them for the winter. By following these simple tips, you can significantly extend the life of your solar pump and ensure that it provides reliable performance for many years to come. Remember, a little bit of maintenance goes a long way.
Choosing the Right Type of Solar Pump: Submersible vs. Surface
When selecting a solar pump, you'll encounter two main types: submersible and surface pumps. Submersible pumps are designed to be placed directly in the pond, while surface pumps are located outside the pond and draw water through a hose or pipe. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to choose the one that's best suited to your pond's specific needs.
Submersible pumps are typically less expensive and easier to install than surface pumps. They are also quieter because they are submerged in the water. However, they can be more difficult to maintain because you have to remove them from the pond for cleaning and repairs. Submersible pumps are also more susceptible to clogging because they are directly exposed to debris in the water. Surface pumps, on the other hand, are generally more efficient and easier to maintain. They are also less susceptible to clogging because they draw water through a filter or strainer. However, surface pumps are typically more expensive and require more complex installation. They can also be noisier than submersible pumps because the motor is located outside the pond.
The choice between a submersible and surface pump will depend on several factors, including the size of your pond, the amount of debris in the water, and your budget. For small ponds with relatively clean water, a submersible pump may be sufficient. For larger ponds or ponds with a lot of debris, a surface pump is generally a better choice. Consider the noise level, maintenance requirements, and installation complexity when making your decision.
Fun Facts About Solar Powered Pond Pumps
Did you know that some solar-powered pond pumps can run even on cloudy days? It's true! While direct sunlight is ideal, many modern solar pumps are designed to operate with reduced performance in diffuse light. This is thanks to improvements in solar panel technology and energy storage capabilities. Think of it like a dimmer switch; the pump may not be running at full blast, but it's still circulating water and keeping your pond healthy.
Here's another fun fact: solar pumps are used in a variety of unexpected places around the world. They're not just for backyard ponds! You'll find them in remote villages providing clean drinking water, in agricultural settings irrigating crops, and even in ecological restoration projects helping to revive wetlands and streams. It's a testament to the versatility and sustainability of this technology.
And finally, did you know that some solar pumps can be controlled with your smartphone? That's right, the world of pond pumps is getting high-tech! With a smart solar pump, you can adjust the flow rate, set timers, and even monitor the pump's performance remotely. It's a convenient way to keep your pond healthy and thriving, even when you're not at home. The world of solar pumps is constantly evolving, with new innovations and improvements emerging all the time. It's an exciting field to watch, and it offers a sustainable and eco-friendly way to enhance the beauty and health of your pond.
How to Install Your Solar Pond Pump
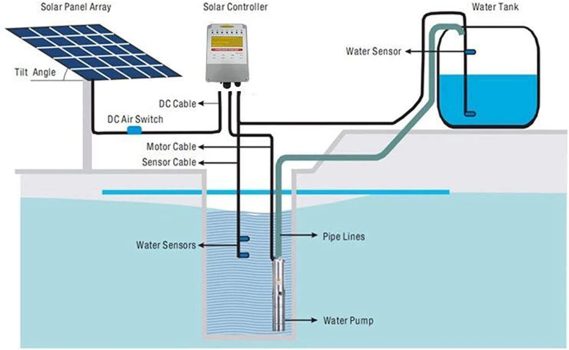
Installing your solar pond pump can seem daunting, but it's actually a straightforward process that most DIY enthusiasts can handle. The first step is to choose the right location for your pump and solar panel. The pump should be placed in a location that allows for easy access for cleaning and maintenance. The solar panel should be placed in a location that receives direct sunlight for most of the day. Avoid placing the panel in shaded areas or near trees that could block the sunlight.
Once you've chosen the locations, you'll need to connect the pump to the solar panel. Most solar pumps come with a pre-wired cable that connects directly to the solar panel. If the cable is not long enough, you can purchase an extension cable from a hardware store. Be sure to use a cable that is rated for outdoor use. Once the pump and panel are connected, you can place the pump in the pond. If you have a submersible pump, simply lower it into the water. If you have a surface pump, you'll need to connect it to a hose or pipe that draws water from the pond.
Secure the hose or pipe to the pump and place the other end in the pond. Make sure the hose or pipe is submerged in the water to prevent the pump from running dry. Finally, secure the solar panel to a pole or bracket. The panel should be angled towards the sun to maximize its efficiency. You may need to adjust the angle of the panel throughout the year to compensate for the changing position of the sun. Once everything is connected and secured, you can turn on the pump and enjoy the beauty of your solar-powered pond. Be sure to monitor the pump's performance and make any necessary adjustments to ensure that it is operating efficiently.
What If Your Solar Pump Isn't Working?
It's frustrating when your solar pump isn't working as expected. But don't panic! Most issues can be resolved with a little troubleshooting. The first thing to check is the solar panel. Make sure it's clean and free from debris like leaves, dirt, or bird droppings. Even a thin layer of grime can significantly reduce the panel's output. Use a soft cloth and water to gently clean the panel. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
Next, check the wiring and connections. Make sure all connections are secure and free from corrosion. Loose connections or corroded wires can prevent the pump from receiving power. If you find any loose connections, tighten them with a screwdriver. If you find any corroded wires, clean them with a wire brush or replace them altogether. If the solar panel and wiring are okay, the next thing to check is the pump itself. Make sure the impeller is clean and free from debris. Debris can clog the impeller and prevent the pump from working. Disassemble the pump and clean the impeller thoroughly. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for disassembly and cleaning.
If the pump still isn't working after cleaning the impeller, the motor may be damaged. In this case, you may need to replace the pump. Before replacing the pump, check the warranty. The pump may be covered under warranty, in which case you can get a free replacement. If the pump is not covered under warranty, you'll need to purchase a new pump. When purchasing a new pump, be sure to choose one that is compatible with your solar panel. Also, make sure the new pump has the same flow rate and head height as the old pump.
Top 5 Benefits of Using a Solar Pond Pump (Listicle)
Here's a quick rundown of the top 5 reasons to switch to a solar pond pump:
- Eco-Friendly Operation: Solar pumps harness the power of the sun, reducing your carbon footprint and promoting a sustainable lifestyle.
- Cost Savings: Say goodbye to expensive electricity bills! Solar pumps operate on free solar energy, saving you money in the long run.
- Easy Installation: Most solar pumps are easy to install and require no complicated wiring or plumbing.
- Quiet Operation: Enjoy the tranquil sounds of your pond without the noise of a traditional electric pump.
- Improved Pond Health: Solar pumps circulate water, preventing algae blooms and creating a healthier environment for your aquatic life.
These are just a few of the many benefits of using a solar pond pump. Whether you're looking to save money, reduce your environmental impact, or simply improve the health of your pond, a solar pump is a great investment. Consider the specific needs of your pond and choose a solar pump that meets those needs. With a little research and planning, you can find the perfect solar pump for your pond and enjoy the many benefits it has to offer.
Question and Answer about Selecting the Right Solar Pump for Your Pond's Size and Needs
Here are some frequently asked questions about choosing the right solar pump:
Q: How do I calculate the correct flow rate for my pond?
A: A good rule of thumb is to circulate the entire volume of your pond at least once every two hours. So, if you have a 1000-gallon pond, you'll need a pump with a flow rate of at least 500 gallons per hour (GPH). However, you may need to increase the flow rate if your pond is heavily stocked with fish or prone to algae blooms.
Q: What is head height, and why is it important?
A: Head height is the maximum vertical distance a pump can push water. It's important if you plan to use the pump for a fountain or waterfall. Measure the vertical distance from the pump's location to the highest point of the fountain or waterfall to determine the minimum head height required.
Q: Do solar pumps work on cloudy days?
A: Many modern solar pumps are designed to operate with reduced performance in diffuse light. However, their output will be lower on cloudy days compared to sunny days. Consider a pump with a battery backup for consistent performance.
Q: What type of maintenance is required for a solar pump?
A: Regular maintenance includes cleaning the pump impeller and solar panel, checking the wiring and connections, and winterizing the system in cold climates. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for specific maintenance procedures.
Conclusion of Selecting the Right Solar Pump for Your Pond's Size and Needs
Ultimately, selecting the right solar pump for your pond is an investment in the health, beauty, and sustainability of your aquatic ecosystem. By carefully considering your pond's size, flow rate requirements, head height, solar panel wattage, and pump type, you can choose a pump that will provide reliable performance for years to come. Embrace the power of the sun and create a thriving pond that you can enjoy for generations.