The traditional take-make-dispose economic model is facing some serious challenges, and you might be wondering if there are practical alternatives that truly make a difference. It can feel overwhelming to think about, but the good news is that a shift is already underway towards a circular economy, and solar power is playing a vital role in this transformation.
Understanding how solar energy fits into this picture can give you a tangible way to contribute to a more sustainable future, and give you confidence that your energy choices can have a real impact. It's not just about generating clean electricity; it's about rethinking how we use resources and minimizing waste at every stage of the process.
Let’s start with a simple, actionable step: consider a home energy audit. Many local utilities offer them for free or at a reduced cost. This will help you identify areas where you can reduce your energy consumption, making the transition to solar even more effective and cost-efficient. Now, let’s dive deeper into how solar power is contributing to a circular economy.
Solar Power's Role in a Circular Economy
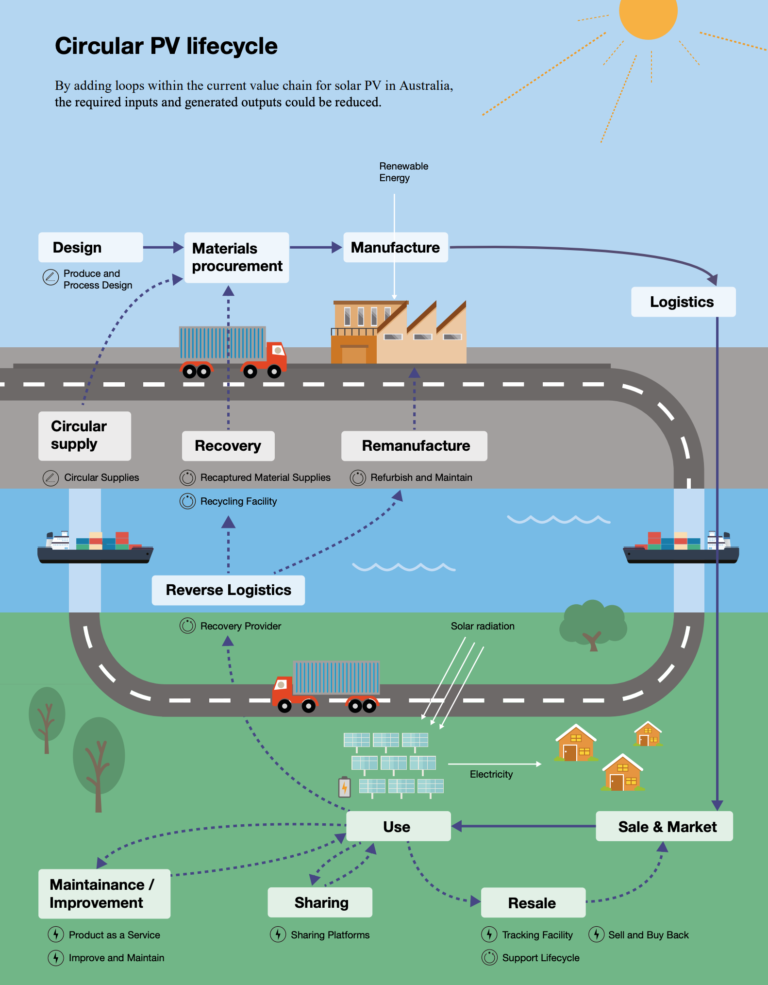
The circular economy is all about minimizing waste and making the most of resources. Instead of the linear model of "take, make, dispose," it emphasizes designing products and systems that can be reused, repaired, repurposed, or recycled. Solar power contributes to this circular model in several key ways, from the materials used in solar panels to the way we manage their end-of-life. Let’s explore these pathways.
Reduced Resource Consumption
One of the most significant ways solar power promotes a circular economy is by reducing our reliance on finite resources. Traditional energy sources, like fossil fuels, are extracted from the earth, burned for energy, and then release pollutants into the atmosphere. This is a linear process with a clear beginning and end, and it leads to resource depletion and environmental degradation.
Solar power, on the other hand, harnesses the energy of the sun, a renewable resource that's virtually inexhaustible. Once a solar panel system is installed, it can generate clean electricity for decades with minimal ongoing resource input. This drastically reduces the need to constantly extract and process new resources for energy production. The energy used to create the panel is offset within a couple years, leaving decades of clean energy production remaining.
Extended Product Lifecycles
Durability is key to a circular economy. Solar panels are designed to last for 25 years or more, some with warranties extending even longer. This long lifespan means that the resources and energy invested in manufacturing a solar panel are spread out over many years of clean energy production, maximizing their value and minimizing the need for frequent replacements. This extended lifecycle contributes significantly to resource conservation and waste reduction.
How long do solar panels really last?
Most manufacturers guarantee a performance level of around 80% after 25 years, but many panels continue to produce electricity at a high level for even longer. The key is to choose high-quality panels from reputable manufacturers and ensure proper installation and maintenance.
Recycling and Repurposing Solar Panels
What happens when a solar panel reaches the end of its useful life? This is where recycling and repurposing come into play. While solar panel recycling is still a relatively new industry, it's rapidly developing and becoming more efficient.
Modern solar panel recycling processes can recover valuable materials like silicon, glass, aluminum, and copper, which can then be used to manufacture new products. This closes the loop, reducing the need to extract virgin materials and minimizing waste sent to landfills.
Repurposing is another promising avenue. Even if a solar panel isn't producing electricity at its original capacity, it may still be suitable for other applications, such as powering small electronic devices or providing energy in off-grid settings. Giving these panels a second life further extends their value and reduces waste.
Designing for Circularity in Solar Technology
Beyond the operational benefits, the design and manufacturing of solar technology are also evolving to embrace circular economy principles.
Material Selection
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on using materials that are more durable, easier to recycle, and less environmentally harmful. This includes exploring alternative materials for solar cell production and reducing the use of hazardous substances in panel construction. Choosing panels from manufacturers committed to sustainable material sourcing is a great way to support this trend.
Modular Design
Modular design is another important aspect of circularity. Solar panels that are designed with modular components can be more easily repaired and upgraded, extending their lifespan and reducing the need to replace the entire panel. This also makes it easier to disassemble and recycle the panels at the end of their life, as the different materials can be separated more efficiently.
What are the advantages of thin-film solar panels?
Thin-film solar panels, while generally less efficient than traditional silicon panels, often have a lower environmental impact due to their simpler manufacturing processes and reduced material usage. They also have potential advantages in terms of flexibility and adaptability, opening up new possibilities for solar energy applications.
Product Stewardship
Product stewardship initiatives are becoming increasingly common in the solar industry. These initiatives involve manufacturers taking responsibility for the end-of-life management of their products, either through direct recycling programs or by partnering with recycling companies. This helps to ensure that solar panels are properly recycled and that valuable materials are recovered.
Overcoming Challenges and Embracing the Future
While solar power offers significant benefits for a circular economy, there are still challenges to overcome.
Improving Recycling Infrastructure
One of the biggest challenges is the need for improved recycling infrastructure for solar panels. Currently, the capacity to recycle solar panels is limited, and the processes can be costly and energy-intensive. Investing in research and development to improve recycling technologies and build more efficient recycling facilities is crucial.
Standardizing Recycling Processes
Another challenge is the lack of standardized recycling processes. Different manufacturers use different materials and construction methods, which can make it difficult to recycle solar panels efficiently. Developing industry-wide standards for solar panel design and recycling would help to streamline the process and reduce costs.
What are the barriers to solar panel recycling?
The main barriers include the cost of recycling, the lack of widespread recycling infrastructure, and the complexity of separating the different materials in a solar panel. However, as recycling technologies improve and the volume of end-of-life solar panels increases, the economics of solar panel recycling are becoming more favorable.
Raising Awareness and Promoting Collaboration
Finally, raising awareness among consumers and promoting collaboration between manufacturers, recyclers, and policymakers is essential. Consumers need to be aware of the importance of solar panel recycling and choose products from manufacturers who are committed to responsible end-of-life management. Collaboration between stakeholders is needed to develop effective policies and regulations that support the growth of the solar panel recycling industry.
The Bigger Picture: A Sustainable Energy Future
Solar power's contribution to a circular economy extends far beyond just recycling solar panels. It's about rethinking our entire energy system and embracing a more sustainable approach to resource management. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, extending product lifecycles, and promoting recycling and repurposing, solar power is helping us move towards a future where resources are used more efficiently and waste is minimized.
By supporting the growth of solar power and advocating for circular economy principles, you can play a role in creating a more sustainable and resilient world for future generations. It's a journey, and every step you take, no matter how small, makes a difference.